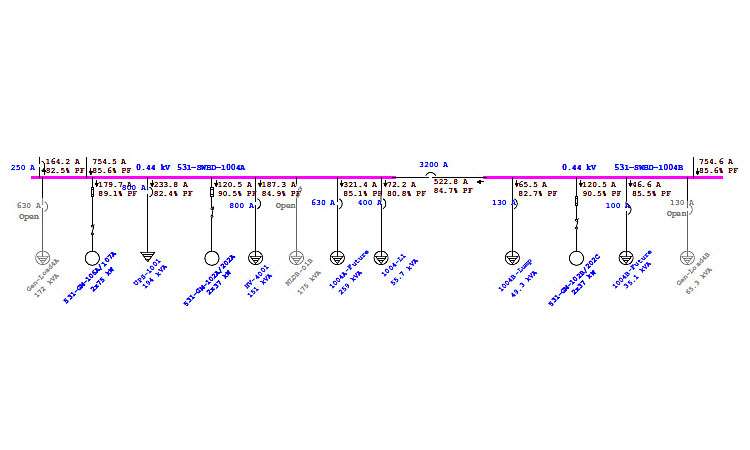
Test and Verify Electrical Motor Efficiency in accordance with Greek Guidelines
Globally, industrial electric motors are utilized in a range of applications. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the car industry consumes up to 70% of all industrial energy, 35% of all commercial and service sector energy, and 45% of all global power production. Each hour of downtime caused by a motor failure costs thousands of dollars, which demonstrates the importance of electric motors in a variety of industrial applications. They are the principal source of climate-altering greenhouse gases. They are also primarily to blame for the significant growth in electricity consumption in emerging countries. There is a global economic opportunity to improve the energy efficiency of industrial motors by 20% to 30%, with most payback periods of less than three years. Electric motors are responsible for approximately 15%, or 4.3 billion tons, of the world’s total annual CO2 emissions of 26 billion tons. Increasing energy efficiency is one of the most cost-effective and low-risk methods for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and slowing the increase in energy usage.
Utilize a Dependable Motor Because:
- Decreased operational costs
- A quieter and cooler run
- Motors with enhanced durability and performance
- There are less emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
How to Start a Vehicle Evaluation:
Electric motors do not usually convert all electrical energy into mechanical energy. Energy loss is caused by friction, windage, and losses in the stator, rotor, and magnetic core. These losses are lowering the efficiency of the motor. Considering how much energy is wasted and how electric motors are utilized in industry, it is easy to see why and how important it is to evaluate efficiency and create minimum energy performance standards. How precisely efficiency and motor loss are determined is dependent on the testing method employed. There is no unique testing technique used by every firm in the globe. Even though the principle is simple, measuring and validating the energy efficiency of a motor using a variety of criteria can be challenging.
Techniques Internationally Recognized for Gauging Effectiveness:
In industrial contexts, the following testing procedures are widely discussed: IEEE 112-2004 is a standard test procedure for multiphase motors and generators. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Publication 60034-2-1, 2014. “Methods for assessing the efficiency and losses of spinning electrical machinery.” JEC 37 is the standard created by the Japanese Electrotechnical Committee for induction devices. IEEE/ANSI 112-2004 IEEE Standard 112-2004
This method contains ten methods for evaluating energy efficiency. To emphasize the most essential:
- Simple input and output tests exist.
- Loss-separated testing of input and output.
- Parallel testing of two interconnected computers.
- Smoothed residual losses are used to compute the load losses.
- The “Eh-star” method
Three main types of IEC standard testing exist:
- Calculating the input and output power of a single machine.
- Monitoring the power entering and leaving two devices that are connected back-to-back.
- The losses of one machine were tallied.
The Japanese JEC standard 37 test techniques entirely overlook the additional load losses. By minimizing the amount of energy used by their equipment and appliances, businesses may save money and help the environment. This is merely one of several substantial economic and environmental benefits. Among other major cities, we provide motor start analysis services in Rome, Milan, Florence, and Venice.
Share Post
Related Posts
-
How to Conduct Power Quality Analysis in Italy
-
Power Quality Working Principles in Italy
-
The Importance of Load Flow and Short Circuit Analysis for a Italian Business
-
Test and Verify Electrical Motor Efficiency in accordance with Italian Guidelines
-
How to evaluate efficiency and dependability of commercial motors?
-
Arc Flash Analysis in Italy: A Detailed Guide
-
Load Flow, Short Circuit, and Relay Coordination in Power System Analysis
-
Why Is Harmonic Analysis and Research Important for Italian Businesses?
-
Arc Flash Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Are Essential
-
Harmonic Examination of the Italian Power System