Load Flow, Short Circuit, and Relay Coordination in Power System Analysis
A power system analysis includes a variety of technical assessments as well as the use of scientific analytical concepts and methods to confirm that the power system at your facility is secure, efficient, and dependable in both expected and unanticipated circumstances. Understanding how a system would behave in various configurations and how disturbances like capacitor switching, the start of a large motor, and arc flash energy will affect it are the goals of a power system analysis. It could be required to examine the power system to ensure that safety equipment operates efficiently in the case of a short circuit or other malfunction. To offer a constant and dependable supply of electricity, power systems must be studied. A well-designed power system guarantees dependable operation and maximizes plant usage under all operational circumstances. Systems with poor construction are characterized by breakdowns, flaws, inefficiencies, and decreased security.
A study of a typical power system may involve the following short studies:
- Study and analysis of load flow
- The concept of short circuits is investigated.
- An investigation into relays’ means of communication.
- Research and analysis on arc flash risk
- Harmonics research
- Analysis of movement and change
- Earth science research
The first three studies will be examined in this blog. and understand the rules and practices that apply to each of these inquiries.
Load Flow Analysis and Investigation:
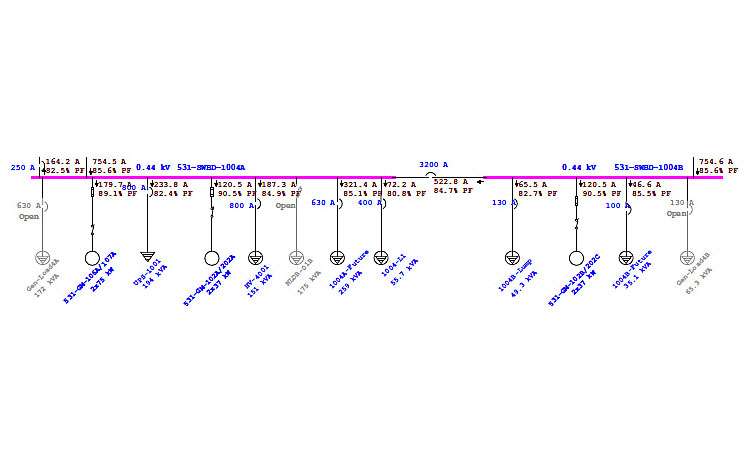
An electrical network is examined in a load flow analysis to determine the direction of power flow. It aids in calculating losses, voltage, current, power factor, active and reactive power generated, and the efficiency of the power system.
The load flow study was divided into three parts:
- Modeling of the networks and parts of the power system
- The process for creating equations for load flow.
- Solving the equations that describe the connection between load and flow mathematically.
There are three techniques to get data on the electricity system:
- One well-known method of data analysis is the Gauss-Seidel System. This approach has the advantages of being simple to use, using minimal computer resources, and completing the task quickly. However, more procedures are required due to the delayed convergence. The number of buses rises in tandem with the number of iterations.
- The Newton-Raphson approach is more complicated and makes use of quadratic convergence, which is useful in scenarios that are challenging to comprehend. This method requires fewer iterations to reach convergence, hence it uses less computer resources. Since regulating transformers and slack bus selection have less of an influence, it is even more precise. The drawback is that programming can be difficult and requires a lot of computer RAM.
- Another method for doing load flow analysis is the Fast Decoupled Load Flow System (FDLF). This method’s main advantage is that it uses less memory. It is frequently used in place of the Newton-Raphson technique for real-time power grid management since it performs computations five times quicker. Only specific circumstances allow this application. It is therefore more challenging to modify it in the electricity sector to take factors like flow or system protection into account.
Short Circuit Analysis and Investigation:
One or more of the following types of short circuits will be examined during a short circuit analysis:
- Line-to-line faults develop when two phases short out at once.
- Only one phase of the ground is affected by a single line-to-ground failure.
- A double line-to-ground fault happens when both phases and the ground are simultaneously shorted.
A brief exists between each of the three phases in a three-phase defect. Once the kind of issue has been identified, drawing a one-line diagram of the power distribution system will be straightforward. Calculate short circuits by using the produced single-line diagram and an impedance diagram with numerical values for the conductor, transformer, and utility source in proportion to the potential voltage that each segment may consume. The transformer multiplier, full-load amps, and short–circuit current may all be calculated. To make sure that the power distribution system has the appropriate safety precautions in place at various locations to prevent accidents and downtime, it is crucial to compare the findings to the equipment ratings.
Relay Coordination Is Considered:
Because coordination systems ensure that relays work promptly, dependably, and selectively to isolate the issue, relay coordination is an essential component of power system safety design. Calculating the number of overcurrent protection devices required in a power system involves coordination analysis. Additionally, it aids in identifying the specifications, configurations, and dimensions required to strike a balance between preserving equipment safety and restricting system function.
Data gathering operations are carried out using software like ETAP (Electrical Transient Analysis Program), which simulates the power system. The fault currents are measured at each electrical site following a short circuit investigation. The effect of equipment failures inside the system is therefore minimized by choosing and configuring the protection devices. The protective device’s time-current characteristic curves are tracked and compared to identify areas where coordination has fallen short. To make sure that protection devices work consistently and only when they need to, adjustments are performed as needed.
The Following Are Some Advantages of Power System Analysis:
- The electrical system has been upgraded.
- Using the right tools with the right power rating.
- Electrical risks will be less dangerous and safer.
- Observe all necessary legal requirements and electrical installation guidelines.
- The suggestion of several tactics to improve the system’s functionality and reliability.
- A record of the current operation of the power system is kept for any forthcoming inspections.
CareLabs offers Load Flow, Short Circuit, and Relay coordination analysis to monitor bus voltage, actual and reactive power flow, system fault conditions, and system response to minor and major changes. If your Spanish company requires a power system audit, please receive a quote. Within 24 hours, one of our customer care representatives will give you a call.
Share Post
Related Posts
-
How to Conduct Power Quality Analysis in Spain
-
Power Quality Working Principles in Spain
-
The Importance of Load Flow and Short Circuit Analysis for a Spanish Business
-
Test and Verify Electrical Motor Efficiency in accordance with Spanish Guidelines
-
How to evaluate efficiency and dependability of commercial motors?
-
Arc Flash Analysis in Spain: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Load Flow, Short Circuit, and Relay Coordination in Power System Analysis
-
Why is Harmonic Analysis and Study Important for Spanish Businesses?
-
Importance of Arc Flash Hazard Analysis and Mitigation Methods
-
Harmonic Analysis in Power System in Spain