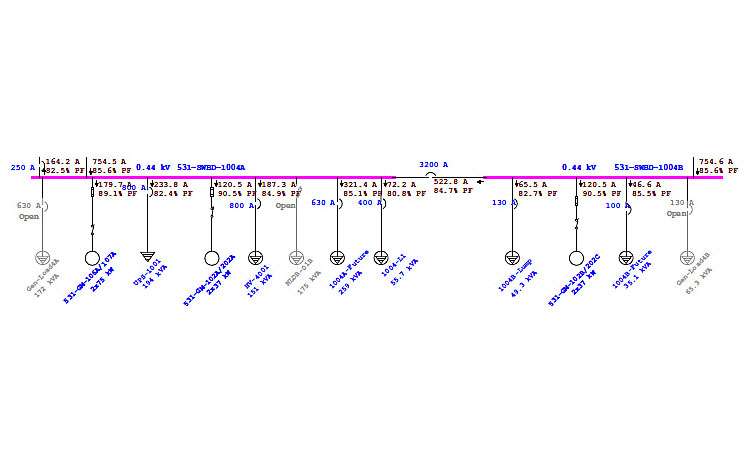
Importance of Arc Flash Hazard Analysis and Mitigation Methods
Electrical arcs can develop when a gas is subjected to a voltage that is higher than what the gas can resist blocking. An arc forms when the voltage between the conductors is high enough to ionize the space in between. Air becomes an excellent conductor of electricity when ions are added to it. Air is heated and illuminated by the current created by air ionization. The ionized air rises from this heat, creating an arch-shaped stream. The phenomena is referred to as an arch current as a result. The temperature of an arc flash can reach 20,000 degrees Celsius.
Risks from arc flashes put both persons and property in danger. Arc in flash has several benefits for companies, including:
- Medical attention, therapy, worker compensation, the cost of an investigation into the occurrence, and lost productivity are examples of direct expenditures.
- Legal and judgment fees, litigation expenses, penalties, insurance premiums, repair fees, and the cost of recruiting a replacement employee are examples of indirect costs.
- Unwanted incidents can damage your reputation, make it more difficult for you to get work, and even lead to criminal prosecution.
- Consumers tend to avoid companies with a lot of accidents, which results in lost revenue and perhaps the cancellation of an electrical license.
- Accidents involving electrical circuit use Flash makes a statement, which might result in missed opportunities and money squandered.
Where Do Arc Flash Threats Come From?
- Using a test probe on an unsuitable surface
- Inappropriate tools, installations, and work practices
- Using substandard electrical components
- Equipment gaps or damage to the insulation
- Dispute over the disconnect panel
- Rust or dust on electrical equipment
- Inadequate switch and circuit breaker maintenance
- Vital organs exposed to the elements or frayed connections
- High-voltage wires or a constant power supply
- Electrical equipment that is damp
Strategies to Reduce the Risk of an Arc Flash
- Making electrical components inactive:
It reduces potential risks as much as is practicable. Equipment that is electrified should not be worked on, and extreme caution should be used while testing it after it has been de-energized or re-energized. Circuit breakers that may threaten the worker operating them are kept from being too near to arc flash boundaries thanks to the usage of remote tracking.
- Make use of technology that provide less risks:
To evaluate the dangers associated with short circuits and the interplay of protective devices, arc flash analysis and power system studies are performed. To safeguard people and property, choose low-threat alternatives such as remote rack equipment.
- Electrical and control system replacement:
Based on the arc flash’s strength, confirm that the appropriate degree of PPE (personal protective equipment) is available. Engineering methods and equipment are changing to become safer. Energy distribution systems and circuit breakers are designed to limit the flow of energy.
- Reduce the available fault current:
Industries will be able to lower the amount of accessible fault current by using non-current limiting breakers. These items can be used with an open tie during maintenance. By reducing the amount of fault current accessible during maintenance, the opening connection between the twin power supply lowers the possibility of an arc flash. Current-limiting reactors can be used to halt the flow of electricity during arc faults.
- Change the blast's energy:
Encourage the use of materials resistant to arcs. Arc-resistant switchgear uses ducts to transfer the heat and energy produced by arc flashes to an empty space. To do this, sealed joints, top pressure release vents, and stronger hinges were used. CareLabs provides a wide range of arc flash investigation and analysis services. Arc flash risks are looked at by experts to make sure your safety program is up to date. CareLabs may use innovative technology to identify arc flash hazards and reduce them. Software called ETAP (Electrical Transient Analysis Program) is used at CareLabs for research and analysis.
To ensure that our professionals are available nearby in case of an emergency or for normal work, CareLabs employs staff members in many locations. CareLabs has quickly made a name for itself as an ISO 9001:2008-accredited business with a powerful reputation and an extensive list of pleased customers. are just a few of the main Spanish Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, and Seville cities where CareLabs provides arc flash testing and analysis.
Share Post
Related Posts
-
Importance of Arc Flash Hazard Analysis and Mitigation Methods
-
Power Quality Working Principles in Spain
-
Arc Flash Analysis in Spain: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Load Flow, Short Circuit, and Relay Coordination in Power System Analysis
-
Why is Harmonic Analysis and Study Important for Spanish Businesses?
-
How to Conduct Power Quality Analysis in Spain
-
Harmonic Analysis in Power System in Spain
-
The Importance of Load Flow and Short Circuit Analysis for a Spanish Business
-
Test and Verify Electrical Motor Efficiency in accordance with Spanish Guidelines
-
How to evaluate efficiency and dependability of commercial motors?