Consequences of Arc Flash Incidents
The importance of Arc Flash Study in Canada begins with a recent report by Ontario’s Labor Ministry indicates that 28 workers have been killed and 255 seriously injured from arc flash incidents in the past ten years. Electrical workers accounted for 21 percent of all electrical-related fatalities.
To know more related Arc Flash Incidents
Injuries not only occur due to the excessive heat energy released but also as a consequence of other non-thermal elements such as pressure, sound, and intense light. A burn from the initial flash is the most common injury. Burns may be deadly at several feet, and severe burns can occur at 10 feet. Heated air and molten arc metal, even in indirect contact with the arc, may ignite a fire. Lung damage may be caused by inhalation of vaporized metal.
Pressure released can be as high as 2,000 pounds a square foot and can cause the lungs to collapse. A high-density flash can injure the eye as well, leading to distortion or full vision loss. The explosion can cause a sound beyond 160 dBA, which causes instant loss of hearing as eardrums rupture. Subsequently, it also causes severe damage to the equipment and surrounding area.
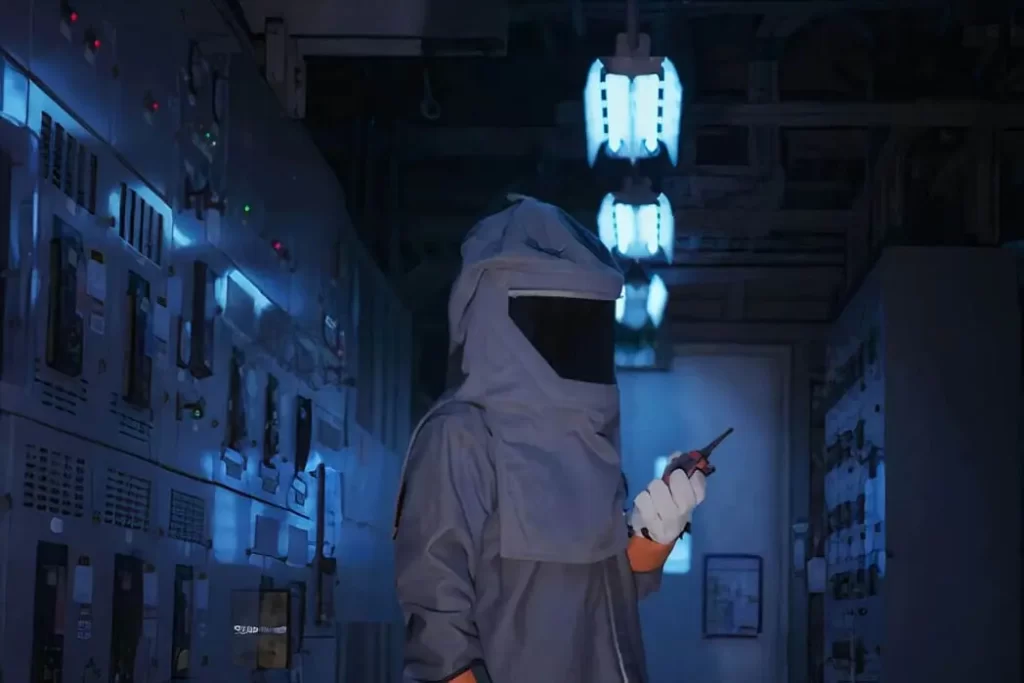
What is an Electrical Arc Flash and How is it Caused?
An arc flash fault occurs when a huge amount of electrical current flowing through the air gap between conductors and ionizes the surrounding air & expels a large amount of energy.
An arc flash hazard can be initiated by a variety of causes, a few of which are:
- Improper installation or substandard parts
- Dropping tools in the facility that can cause a spark or accidental contact of the tool with live parts
- Dust, ashes, or other impurities on the conductor’s surface.
- Live sections and holes that are exposed.
- Wear and tear, corrosion, and moisture are also factors to consider.
- Electrical contact points that have deteriorated or areas of loose connections
- Non-periodic inspection and maintenance
- Lack of electrical safety awareness and training
Arc Flash Hazard Analysis and Mitigation Strategies:
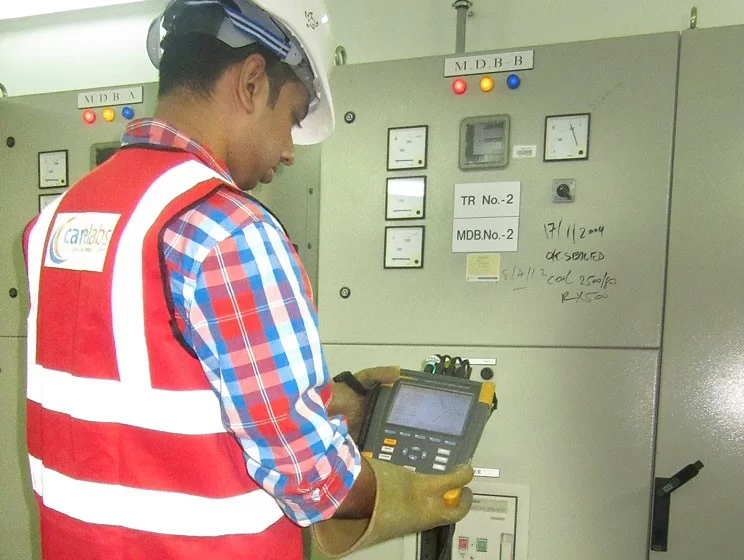
Arc flash hazard analysis involves assessing the potential risks associated with arc flash incidents in a facility. Arc Flash analysis typically includes:
- Identification of Potential Hazards, Arc Flash Boundary Determination, Arc Flash Energy Calculation, Equipment Labeling and Engineering Controls Assessment.
- By carrying out arc flash analysis the risk can be minimized. It will help categorize the hazard on the equipment based on the incident energy.
- The arc flash protection boundary is also identified. A worker must wear adequate personal protective gear in the arc flash protection boundary.
- Our work process includes data collection, power system modeling using ETAP, short circuit & coordination study, arc flash assessment, and evaluation.
Studies can also be customized to include the following:
- Analysis of fault current and coordination
- Recommendations for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Arc flash labeling in equipment and enclosure
- Arc flash mitigation strategies
- Written procedures on electrical safety
What Protective Measures can be Taken?
Before starting operations, the only assured method to prevent arc flash is to de-energize the system or equipment. The possibility for an arc incident must be evaluated and hazard analysis must be performed before commencing work on an energized system. The risk assessment sets forth three approach limits, each with distinct worker protection needs. These limits are dependent on voltage levels, the fault current, time to operate and clear up the fault by a protective device, and distance from the live component.
- Unless guided by a certified person, no unskilled individual is allowed to come close to the installation. To cross the limited approach boundary, a qualified individual should have suitable personal protective gear and training to carry out the necessary task.
- Only a qualified employee who has undergone training and also possesses adequate PPE can cross a restricted approach boundary. This person must also have an authorized written plan of work he/she will perform.
- Prohibited approach boundary work is carried out under the same criteria as the restricted approach boundary, considering that the crossing is the same as contacting exposed live conductors or circuit sections.
Commercial and industrial electrical systems are frequently susceptible to arc flash hazards. Performing Arc Flash Hazard Analysis will increase personnel safety and reduce arc flash injuries.