Issues such as voltage sags and surges, transients, and harmonics are estimated to cost Canadian companies about $ 1.2 billion in production losses each year, and about $140 million a year in B.C according to research by the Canadian Electrical Association.
You should understand the symptoms and causes of harmonics, and how to effectively eliminate harmonics in the electrical system of the factory so that the enterprise can operate effectively.
Care Labs offers harmonic analysis services intending to identify the source of harmonic distortions, predicting the impact of the harmonic distortion, and recommending solutions to combat this power quality issue.
What are harmonics?
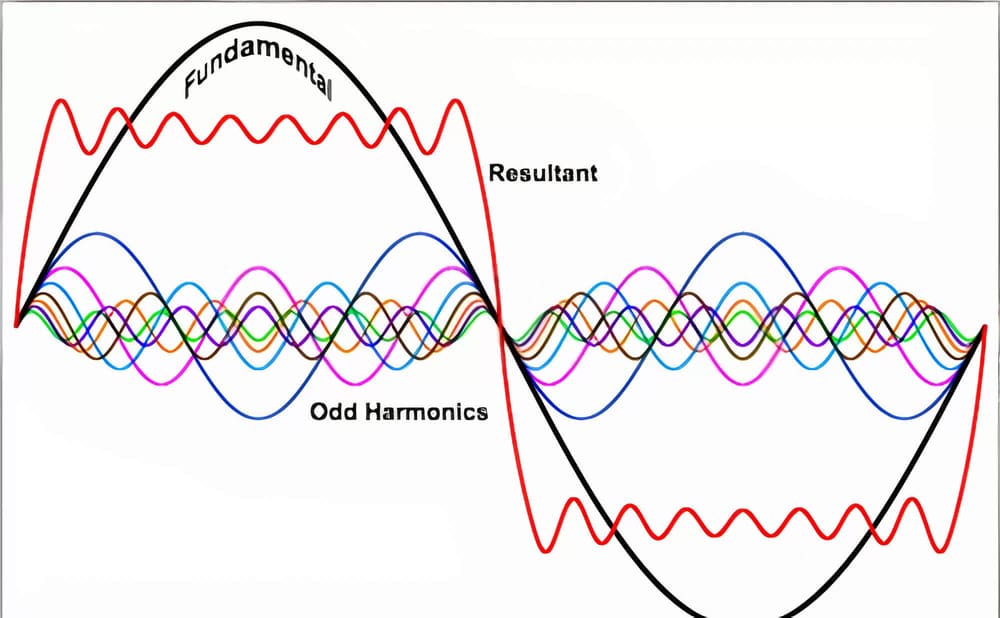
Harmonics are the voltage and current in the power system, which can cause power quality problems.
Since equipment and machinery may malfunction or malfunction under the action of high levels of harmonic voltage and/or current, harmonic distortion is an increasingly serious problem for factory managers, automation equipment users, and engineers.
Causes of harmonics:
Harmonics are generated by “non-linear” loads in the power system. The current drawn by the non-linear load is proportional to the applied 60 Hz sinusoidal voltage. In other words, the device “gulps” the current in the power supply instead of absorbing the current smoothly.
Non-linear loads that generate harmonics come from power electronic equipment, such as:
- Computer equipment
- Adjustable Speed Drive (ASD)
- Consumer electronics products
- Electronic lightning ballasts
- Battery chargers and welders.
Effects of harmonics:
- Harmonic level amplification is caused by series and parallel resonance.
- Due to the following reasons, the efficiency of power generation, transmission, and utilization has decreased
1)Increase in loss (loss of iron and copper)
2)Harmonic torque of an asynchronous motor
- The insulation of electrical components is aging and reduces its service life.
- Equipment failure, for example:
1)Frequency or waveform sensitive equipment (adjustable speed drives,…)
2)Relays and protection devices (third harmonic impedance)
- metering device
- Interference with the operation of control equipment (PF control, electronic circuits).
- For multi-grounded power distribution systems with line-to-neutral loads, the third harmonic current will cause special problems.
- Interference with the communication system.
Reference standards:
- IEEE 3002.8-2018
- IEEE Std 519-2014
How to eliminate harmonics:
Although there are several products on the market for dealing with harmonics, each product requires careful analysis to ensure proper use. Both passive and active harmonic filters can be applied in specific situations.
Passive harmonic filters are the most common and are always custom-designed for the application or site. Active harmonic filter is a relatively new technology, and because its initial cost is competitive with passive filters, it will quickly gain market share.
What is done during harmonic analysis?
Harmonic analysis or harmonic modeling is an algorithm that predicts potential resonance and harmonic distortion levels based on available power system data. Except for the simplest system, all other systems require a computer to perform this analysis.
There are several software packages dedicated to this purpose.
Devices such as transformers, capacitors, and power system impedance are considered, and nonlinear loads are represented by multiple current sources of harmonic frequencies. Such simulation studies will show whether the harmonic levels are within IEEE or utility limits.
There are two types of analysis for harmonic study and analysis:
Current and voltage distortion analysis.
Evaluate individual and total current and voltage harmonic distortions on multiple channels, and then evaluate the results according to the specified limits.
Impedance and frequency analysis
Plotting of the dependence of system impedance on frequency on different buses. This analysis is very important for predicting system resonance before energizing the electrical system.
An increase in the impedance diagram indicates parallel resonance, and a decrease in the impedance diagram indicates series resonance.
If the harmonic analysis shows that there are extremely high harmonic levels or potentially dangerous resonance conditions, many alternative corrective measures can be taken.
- Install a rectifier with more than 6 pulses.
- A small amount of power factor correction capacitance should be relocated or disconnected to ensure that a resonant frequency has shifted away from a characteristic harmonic.
- Harmonic filters can also be added to the system.
- Implementation of pulse width modulation (PWM) rectifier.
Advantages of harmonics analysis:
- Higher system efficiency
- Suppresses the amplitude/frequency of power fluctuations
- Add solutions to mitigate power quality issues
- Harmonic preventive measures
- Reduce responsibility for electrical equipment failures.
- Avoid load and line loss.
It is always a safer option to identify underlying harmonic distortions and resolve the cause. Care Labs provides a comprehensive harmonic analysis inspection and risk assessment.
Book your harmonic analysis or get a quote for your company today!